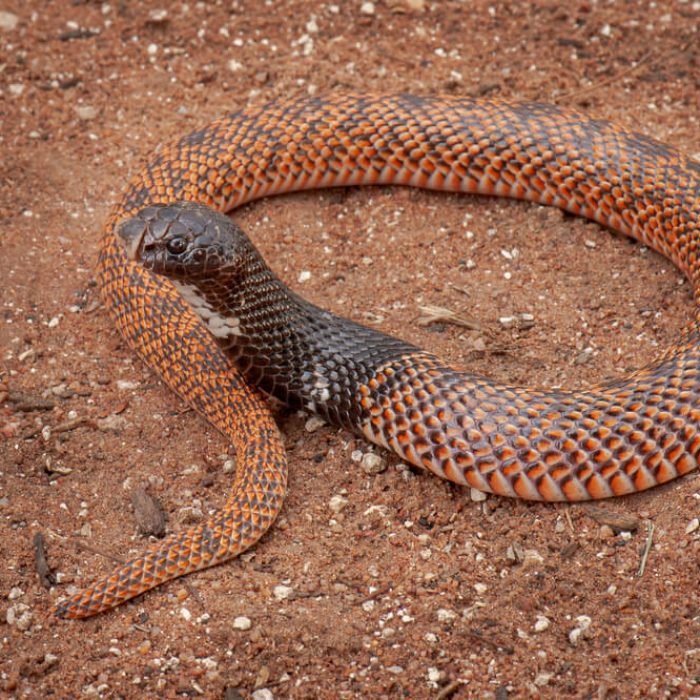
Shield-nosed Cobra
( eastern shield-nose snake or Speckled Shield Cobra )
- Aspidelaps scutatus
- IUCN Status: Least Concern
- Threat: Very deadly
- Venom/Toxin: neurotoxic venom
- Trend: stable

General Information
The shield-nosed cobra (Aspidelaps scutatus) is a species of venomous snake of the family Elapidae. The species is native to southern Africa. There are three recognized subspecies.
Description
Adults of Aspidelaps scutatus have an average snout-to-vent length (SVL) of 63.5 cm. The dorsal scales are arranged in 21–25 rows at midbody, and they are keeled on the posterior portion of the body.
Fun Facts
The species Aspidelaps scutatus is highly venomous, and its bite has caused at least one reported death of a human, despite its propensity to bite being somewhat low. The venom is highly neurotoxic. Symptoms include slurred speech, ptosis, and partial paralysis. No antivenin is available for this species. Any bite or spit-sprayed venom from any elapid snake should be treated as an urgent medical emergency.
Ecology & Behaviour
Aspidelaps scutatus is fossorial. A specialized skull structure, along with the uniquely large rostral scale, make it very effective at digging and tunneling. It is a nocturnal species.
Aspidelaps scutatus can survive between 20 and 28 years in captivity, though this age is normally not attained in the wild due to predation, accidents, etc.
Diet
Aspidelaps scutatus preys upon suitably sized amphibians, lizards, snakes, and mammals.
Reproduction
Aspidelaps scutatus is oviparous. Clutch size is 4–10 eggs, and the female may stay with her eggs, coiled around them.
Distribtion & Habitat
The shield-nosed cobra is found in Botswana, Eswatini, Lesotho, Malawi, Mozambique, Namibia, South Africa, Zambia and Zimbabwe.
The preferred natural habitat of Aspidelaps scutatus is sandy-soiled savanna, at altitudes of 90–1,400 m.
References
Share:
- Phylum: Chordata
- Class: Reptilia
- Order: Squamata
- Suborder: Serpentes
- Family: Elapidae
- Genus: Aspidelaps